
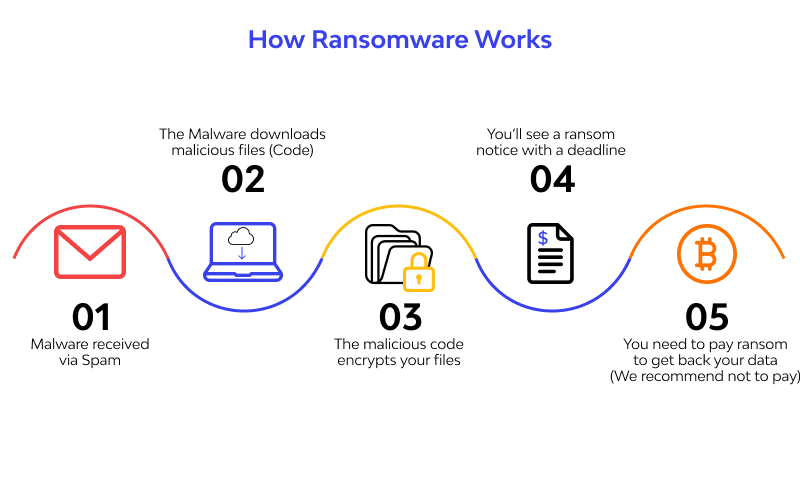
Ransomware is a type of computer virus that encrypts then locks data or structures, averting the user from retrieving them. By encrypting records besides systems, it grasps them hostage. After paying the ransom, the victim receives the decryption key, allowing him to access the locked data or systems (showing in Fig 1).
Ransomware has worried individuals and, more importantly, companies for more than 30 years. Worse, they’ve developed over time into more advanced and sophisticated threats [1][2]. Ransomware is one of the most serious threats in the digital world, according to the FBI and Europol. Certainly, the European agency claims that ransomware has been a major cybercrime concern for some years. According to the US government, there were around 2,474 ransomware attacks worldwide in 2020, resulting in losses of more than USD 29 million.
The technology link with the customer, email system, and the technology connection with the providers are the three main entrance points where ransomware may disrupt the business operations. We have a direct access point to ransomware assaults through the consumers if we have customer-facing web servers for the e-commerce or VPN. Second, ransomware may be delivered by spam emails containing Word or Excel attachments, or via RDP brute force assaults. Third, owing to their lack of attentiveness, certain companies in the supply chain may find themselves unable to provide or fully reconcile with us, as a result of a ransomware assault on their systems [3].
Groundbreaking Ransomware Attacks : There are quite a lot of ransomware attacks that took place earlier this year [4]. Some of these are;
CNA : On March 21, a ransomware assault targeted one of the country’s largest insurance companies, triggering a network outage. CNA called it a “sophisticated cyberattack” in a statement on its website, and said it took “rapid action by proactively disconnecting systems” from the CNA network out of an abundance of caution.
Applus : Applus Technologies, which offers testing equipment to state vehicle inspection stations, was hit by ransomware at the end of March, causing its systems to be down for weeks. Inspection services were brought offline in a number of states as a result of the attack.
Colonial Pipeline : DarkSide, the hacking gang that hacked Colonial Pipeline, also targeted Brenntag, a chemical distribution firm, around the same time in early May 2021. DarkSide sought the equivalent of $7.5 million in bitcoin after obtaining 150 GB of data. Brenntag eventually gave in to the demands and paid $4.4 million. Despite being less than half of the initial demand, it remains one of the largest ransomware payments in history.
Acer : In May of this year, the Revile hacking gang, which was also responsible for an attack on London foreign exchange business Travelex, targeted the computer maker Acer. The ransom of $50 million was the greatest known to date. To get access to Acer’s information, malicious hackers exploited a weakness in a Microsoft Exchange server, leaking photos of crucial financial papers and spreadsheets.
NBA : Ransomware attacks target businesses and organizations across a wide range of industries. The National Basketball Association was one of the more surprise entries on the list this year (NBA). The hacking organization Babuk claimed to have obtained 500 GB of secret data about the Houston Rockets in mid-April of this year. If their demands were not granted, Babuk stated that these sensitive records, including financial information and contracts, would be made public. No ransom payments have been made as of this writing.
New generation product solution : Traditional antivirus software is elevated to a new, sophisticated degree of endpoint security protection with Next-Generation Antivirus [5][6]. Neridio is a new generation of anti-ransomware software, providing tips to be prevented from the Ransome attack showing in Fig 2.

This new-generation anti-ransomware is a system-centric, cloud-based approach, it drives out there established file-created malware signatures besides heuristics. It blends threat intelligence with predictive analytics powered by machine learning and artificial intelligence to:
- Malware and file less non-malware assaults are detected and prevented.
- Unknown sources of malicious activity and TTPs should be identified.
- To uncover fundamental causes, collect and evaluate detailed endpoint data.
- Respond to previously unnoticed new and developing dangers.
Conclusion : Ransomware assaults exist in a variety of sizes and shapes, and they take many different forms. The attack vector has an impact on the type of ransomware used. When calculating the scale and breadth of an attack, it’s critical to keep in mind what’s at stake or what data may be wiped or disclosed. Regardless of the type of ransomware, backing up data and correctly deploying security measures may significantly reduce the severity of an attack.
